File System Implementation¶
- File system resides on secondary storage
Layered File System¶
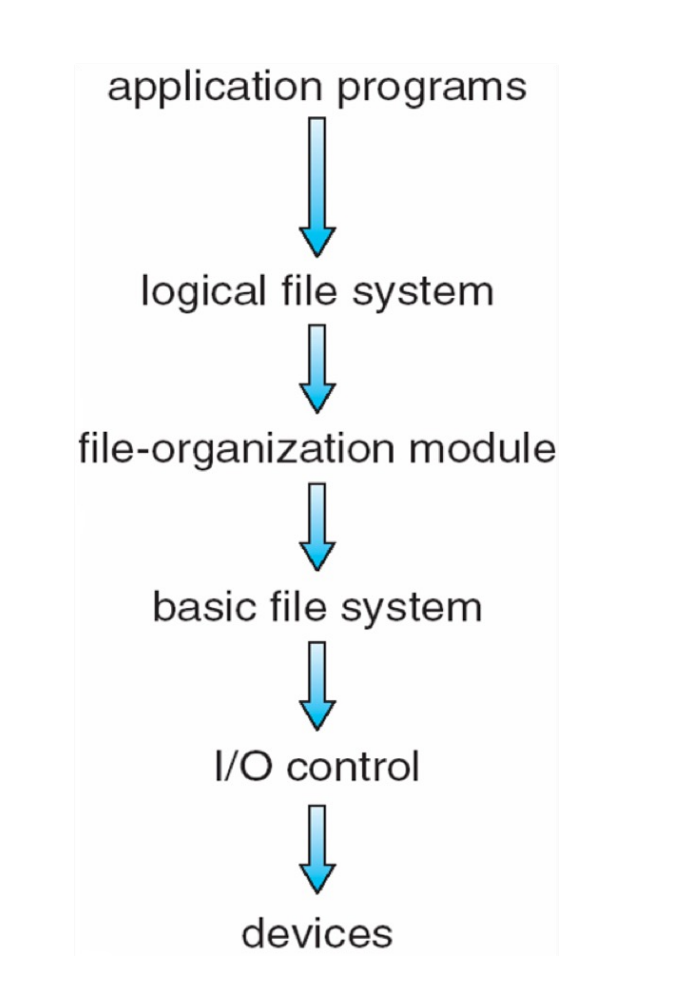
-
Logical file system
-
Keep all the meta-data necessary for the file system
- It stores the directory structure
- It stores a data structure that stores the file description (File Control Block - FCB)
- Input from above:
- Open/Read/Write filepath
-
Output to below:
- Read/Write logical blocks
-
File-organization module
-
Knows about logical file blocks (from 0 to N) and corresponding physical file blocks: it performs translation
把逻辑块映射到物理块。输入是逻辑块号,输出是物理块号。
-
It also manages free space
-
Basic file system
-
Allocates/maintains various buffers that contain file-system, directory, and data blocks.
提供 buffer,用于缓存文件系统、目录和数据块。在 Linux 中称为 IO buffer。
-
I/O Control
Device drivers and interrupt handlers.
I/O control 将上层的指令转换为 low-level, hardware-specific 的指令来实现相关操作。同时也可以发中断。
分层是为了降低复杂度,通过接口来隔离不同层。但也降低了性能。
File System Data Structures¶
on-disk 的是可持久化的(persisitant),in-memory 的是易失的(volatile)。
- On-disk structures
- An optional boot control block
- A volume control block
- A directory
- A per-file File Control Block (FCB)
- In-memory structures
- A mount table with one entry per mounted volume
- A directory cache for fast path translation (performance)
- A global open-file table
- A per-process open-file table
- Various buffers holding disk blocks “in transit” (performance)
File Control Block¶

- ext2_inode:前面是metadata,后面指针指向data,overhead很大

- File Creation:
-
Logical file system allocates a new FCB
-
Appropriate directory is updated with the new file name and FCB
- Operations - open() and close()
-
系统调用
open()将文件名传给 logical file system,后者搜索 system-wide open-file table以确定该文件是否正在被其他进程使用。 -
如果有,则直接在当前进程的 per-process open-file table 中新建一个 entry,指向 system-wide open-file table 中的对应项即可。
-
否则,需要在 directory 中找到这个 file name,并将其 FCB 从磁盘加载到内存中,并将其放在 system-wide open-file table 中。然后,在当前进程的 per-process open-file table 中新建一个 entry,指向 system-wide open-file table 中的对应项

- 图(b)中的index就是我们read/write传入的参数fd
- 同一个process的不同thread之间共享
- system-wide open-file table中每一条都有一个open count记录开了几次
- close一个时,从per-process open-file table移去对应entry,减少一个open count
- open count清零时从system-wide open-file table移去
- 在 Unix 里面(UFS)System-Wide Open-File Table 会放设备、网络,所以我们的设备也是用文件来表示的,读写文件相当于读写设备。
- inode numbering system is only unique within a given file system
Virtual File Systems¶
操作系统可以handle各种类型的文件系统
Linux通过定义统一的接口并在下层实例化为具体操作来实现VFS

- VFS provides an object-oriented way of implementing file systems
操作系统为所有文件系统设置了一套统一的interface,所有的system call都基于这套interface实现
- Linux defines four VFS object types:
-
superblock: defines the file system type, size, status, and other metadata
-
inode: contains metadata about a file (location, access mode, owners…)
-
dentry: associates names to inodes, and the directory layout
-
file: actual data of the file
- VFS的大多数interface都是指针,指向对应文件系统真正实现的部分

-
Write syscall -> vfs_write -> indirect call -> ext4_file_write_iter

-
when is file->f_op setted?
- 在我们open这个文件的时候,
file->f_op就被设为了对应的函数表的地址(f_op是指针)。
- 在我们open这个文件的时候,
Directory Implementation¶
Directory is a special file, storing the mapping from file name to inode.
他的数据块有自己的名字(目录项 dir_entry),每一个目录项有一个 inode号、目录项长度、文件名长度和文件名。
d_entry从人能读懂的文件名转换成计算机能识别的
目录的data block中装的是路径
一般4byte对齐
目录项长度:方便查找,不符合直接跳过,用空间换时间
为hard link

最简单的实现方式是 linear list,即维护 dir_entry[]。这种方案的缺点是查找文件很费时。
使用有序数据结构(有序表、平衡树、B+ 树等)能够优化这一问题。
使用 hash table 也可以解决这一问题。
创建一个文件:首先找到当前目录的 inode,在其指向的数据块里加上一个目录项。(在之前要先分配一个 inode 随后才能放入目录项)
Disk Block Allocation¶
Files need to be allocated with disk blocks to store data
Contiguous Allocation¶
Each file is in a set of contiguous blocks
Good because sequential access causes little disk head movement, and thus shorten seek times
缺点是会碎片化(external fragmentation),同时文件如果增大需要重新分配空间
Linked Allocation¶
Each file is a linked list of disk blocks
Blocks may be scattered anywhere on the disk (no external fragmentation, no compaction)
缺点:搜索很慢,I/O很高,pointer很浪费空间,reliability不高,如果一个pointer被corrupt,当前及其往后的都找不到了
改进: cluster the blocks - like 4 blocks
FAT (File Allocation Table) uses linked allocation DOS
Indexed Allocation¶
Each file has its own index blocks of pointers to its data blocks
用一个块只做 index,里面存放指向数据块的指针。
- Index table provides random/direct access to file data blocks
- No external fragmentation, but overhead of index blocks
- Allows holes in the file
- Index block needs space - waste for small files
需要一个方法分配 index block 的大小(太大会浪费,太小那么指向的空间小)。我们可以把 index block 链接起来,或者用多级索引
如果 block size 为 4KB,那么 Linux 中能创建的最大文件大小为 4TB+4GB+4MB+48KB。如果我们有一个 10KB 的文件,那么只需要前 3 个 direct pointer 就可以,后面的指针都是 NULL,不需要展开。
Free-Space Management¶
Bitmap¶
Use one bit for each block, track its allocation status
相对容易找到连续的block 需要额外的空间

Linked Free Space¶
Keep free blocks in linked list
- No waste of space, just use the memory in the free block for pointers
找到一个空的很方便
- Cannot get contiguous space easily
-
Allocating multiple free blocks require traverse the list
-
Usually no need to traverse the entire list: return the first one

Grouping and Counting¶
- Grouping: use indexes to group free blocks
- Store address of n-1 free blocks in the first free block, plus a pointer to the next index block
- Allocating multiple free blocks does not need to traverse the list
- Counting: a link of clusters (starting block + # of contiguous blocks)
- Space is frequently contiguously used and freed
- In link node, keep address of first free block and # of following free blocks
File System Performance¶
To improve file system performance:
-
Keeping data and metadata close together
-
Use cache: separate section of main memory for frequently used blocks
-
Use asynchronous writes, it can be buffered/cached, thus faster
-
Free-behind and read-ahead: techniques to optimize sequential access - remove the previous page from the buffer, read multiple pages ahead
Page Cache¶

A page cache caches pages for MMIO, such as memory mapped files
A unified buffer cache uses the same page cache to cache both memory-mapped pages and disk I/O to avoid double caching
File and Directory in Practice¶
-
Two Key Abstractions
-
File
-
linear array of bytes
-
has a low-level name - inode number
-
通常OS不知道每个文件的具体类型
-
-
Directory
- 包含一系列low-level的用户可读的名字
- 每个entry指向对应文件或其他目录
-
fd - fd=0 stdin - fd=1 stdout - fd=2 stderr - 因此用户能用的从fd=3开始
-
when removing files, using
unlinkat,unlink(AT_FDCWD, "tmp", 0)for example -
Link - A file may be known by more than one name in one or more directories. - Such multiple names are known as links. - Two kinds of links are also known as hard links and soft links. - Hard link 不能跨文件系统
- A hard link is a directory entry that associates with a file
- The file name “." in a directory is a hard link to the directory itself
- The file name ".." is a hard link to the parent directory
- 以上两个文件对任何都有,因此创造一个目录就会有这两项
- 同时如果父文件夹还存在其他子文件夹,那么这些子文件夹的
..也会对这个文件夹产生hard link - hard link时link后的两个文件inode一样
- 删除最后一个hard link,对应的文件也就从磁盘中删除了
- ln命令
- Soft link (a.k.a., Symbolic link or symlink) 可以跨文件系统
- A symbolic link is a file containing the path name of another file
- Soft links, unlike hard links, may point to directories and may cross file-system boundaries
ln -s f1 f2,将f1 link到f2,从而f2指向f1- hard link更经济,现在用的更多
进程:OS进行资源分配调度的基本单元
线程:执行单元
An Example of FS Organization¶
- suppose 64 blocks, size 4KB
- 需要存的有data, inode, bitmap(一个inode bitmap,一个data region bitmap), 以及一个superblock
- 56个用来存data
- 5个用来存inode。假设inode是256bytes,一个block可以存16个,5个一共可以支持80个inode,因此最多存80个file或directory


df -i指令查看可用和当前使用inode数量
Example¶

- 第一个read找到root的data block,之后遍历directory entry,找到foo的,之后read foo inode以找到data block,遍历directory entry,找到后read bar的inode
- 之后
read,write的时候更新access time

create的时候和上文类似,遍历foo的目录项找不到bar,因此read inode bitmap,发现有可以写的地方后write,之后在foo中写入bar对应的目录项,并初始化bar的inode,最后更新foo(即父目录)的inode的metadatawrite的时候首先read bar的inode,之后read data bitmap查看是否可以写,并写入,再写入bar的data block

